Beginner’s Guide to WordPress Gutenberg Editor – WordPress, the world’s most popular content management system (CMS), underwent a significant transformation with the introduction of the Gutenberg editor. Replacing the classic editor, Gutenberg offers a block-based approach to content creation, providing a more intuitive and flexible way to build web pages. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essentials of the Gutenberg editor, empowering you to create stunning and engaging content with ease.
Understanding the Gutenberg Block Editor
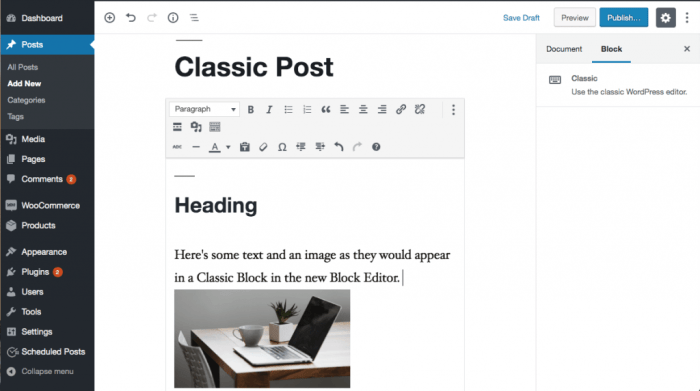
At its core, the Gutenberg editor is a block-based system. This means that instead of working with a single, continuous text field, you build your content using individual blocks. Each block represents a specific element, such as a paragraph, heading, image, or video. This modular approach allows for greater control and flexibility in content arrangement and styling.
Key Features of the Gutenberg Editor:
- Intuitive Interface: The editor’s drag-and-drop functionality makes it incredibly user-friendly, even for beginners.
- Block Variety: A vast library of blocks is available, catering to various content needs, from simple text to complex layouts.
- Customization Options: Each block offers extensive customization options, allowing you to fine-tune the appearance and functionality of your content.
- Real-time Preview: See your changes instantly as you work, eliminating the need for constant preview refreshes.
- Extensibility: Thousands of plugins extend Gutenberg’s functionality, adding even more blocks and features.
Getting Started with Gutenberg: Your First Post
Let’s create your first post using the Gutenberg editor. After logging into your WordPress dashboard, navigate to Posts > Add New. You’ll be greeted by the Gutenberg editor interface.
Adding and Editing Blocks:, Beginner’s Guide to WordPress Gutenberg Editor
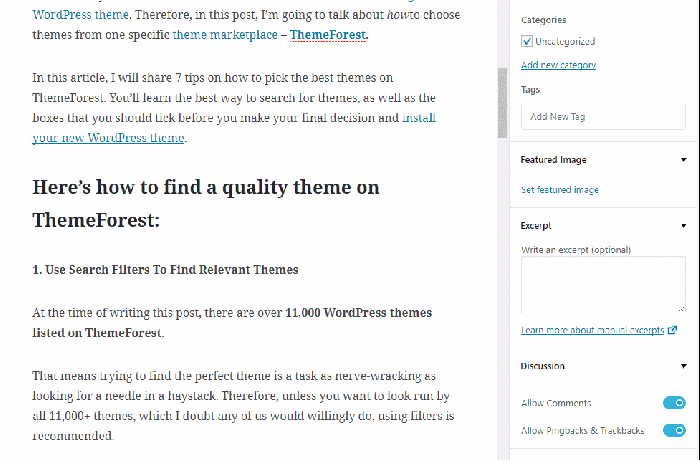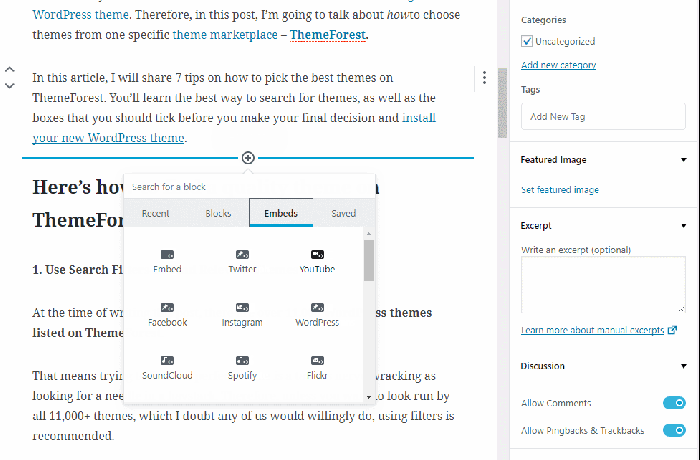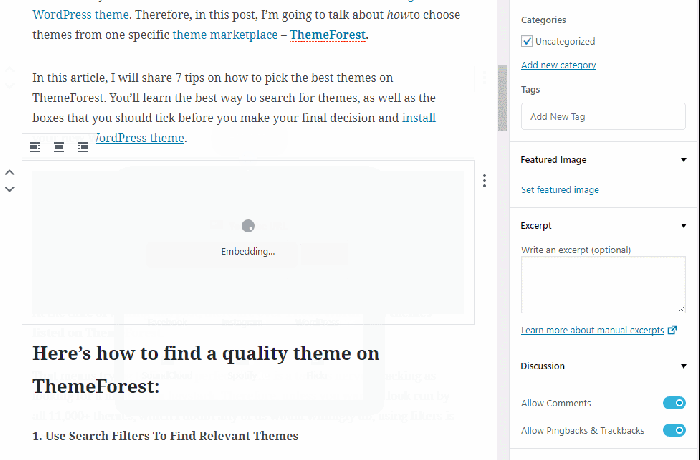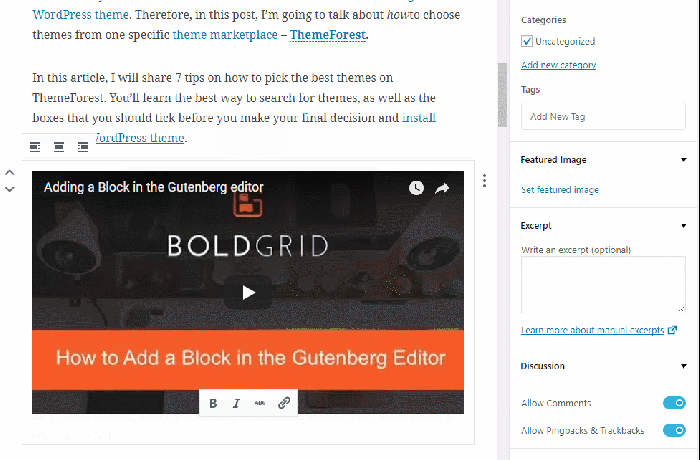
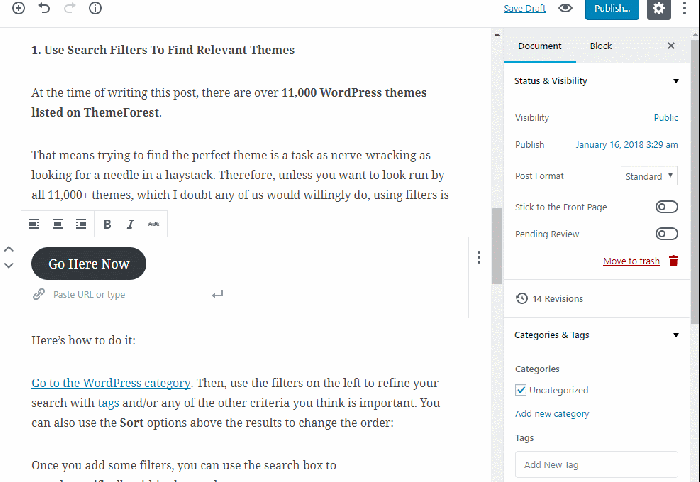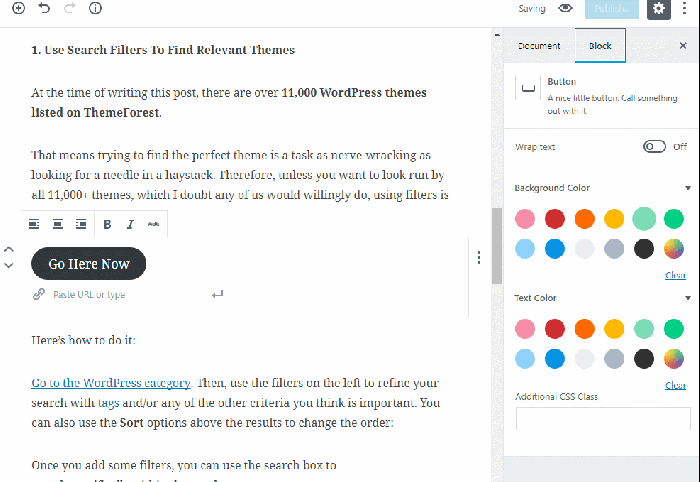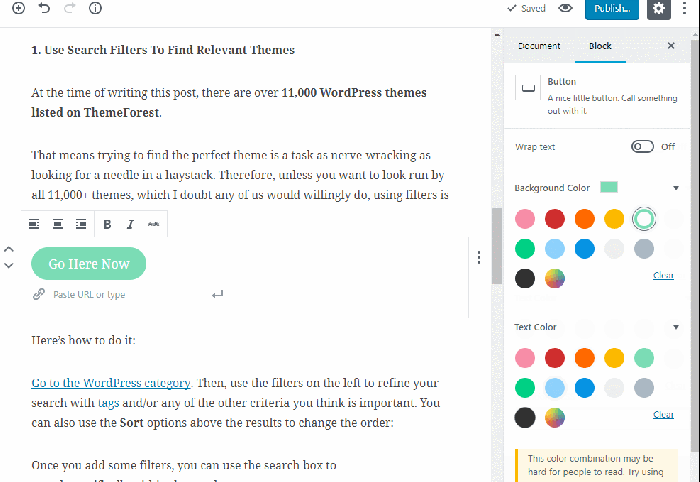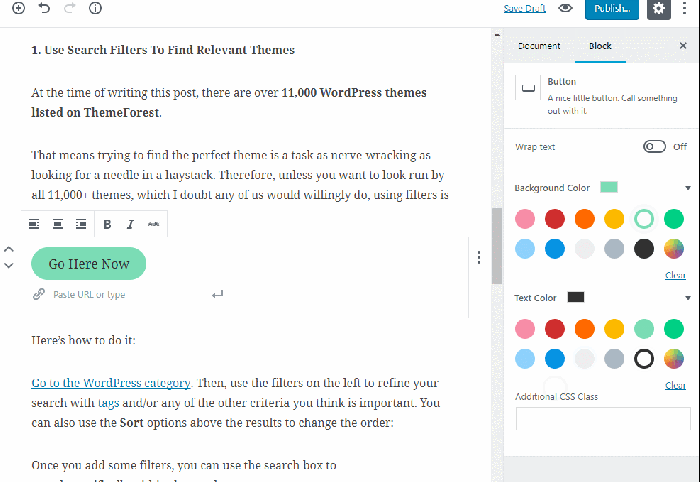
The most fundamental aspect of Gutenberg is working with blocks. To add a new block, simply click the “+” icon. This will open the block inserter, showcasing the available blocks. Select the block you need (e.g., Paragraph, Heading, Image). Once added, you can edit the block’s content directly within the editor.
Many blocks offer additional settings. Click on the block to reveal the block settings in the right-hand sidebar. Here, you can adjust attributes such as font size, color, alignment, and more, depending on the block type.
Working with Common Blocks:
- Paragraph Block: The foundation of most content. Use this for writing text.
- Heading Block: Use these to structure your content with headings (H1-H6).
- Image Block: Easily upload and insert images into your posts. You can add alt text (essential for ) and captions.
- Gallery Block: Create image galleries to showcase multiple images.
- Video Block: Embed videos from platforms like YouTube and Vimeo.
- List Block: Create both ordered (numbered) and unordered (bulleted) lists.
- Quote Block: Highlight important quotes or citations.
Mastering Gutenberg’s Advanced Features
Beyond the basics, Gutenberg offers a range of advanced features to enhance your content creation workflow:
Reusable Blocks:
Create and save custom blocks for reuse across multiple posts and pages. This saves time and ensures consistency in your design.
Source: shoutmeloud.com
Block Patterns:
Gutenberg provides pre-designed block layouts (patterns) to quickly create complex content structures. This is ideal for creating consistent layouts across your website.
Customizing Blocks with CSS:
For advanced users, you can customize the appearance of blocks using custom CSS. This allows for precise control over the visual styling of your content. (Note: This often requires familiarity with CSS and may necessitate using a child theme to prevent losing customizations upon theme updates.)
Source: co.za
Optimization with Gutenberg
Search Engine Optimization () is crucial for online visibility. Gutenberg facilitates through several features:
Using the Right Headings:
Structure your content with appropriate heading blocks (H1-H6) to improve readability and . Use H1 for the main title, H2 for subheadings, and so on.
Adding Alt Text to Images:
Always add descriptive alt text to your images. This helps search engines understand the image content and improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
Using Internal and External Links:
Strategically use internal links (linking to other pages on your website) and external links (linking to relevant resources) to improve navigation and .
Troubleshooting Common Gutenberg Issues
While Gutenberg is generally user-friendly, you might encounter some issues. Here are solutions to common problems:
- Blocks not appearing: Ensure all plugins are up-to-date and check your browser’s cache.
- Unexpected layout issues: Try deactivating plugins one by one to identify potential conflicts.
- Slow loading times: Optimize images and use a caching plugin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Can I revert back to the classic editor? A: Yes, but it’s generally recommended to learn Gutenberg as it’s the future of WordPress editing. Plugins are available to temporarily switch back, but long-term usage of the classic editor is discouraged.
- Q: How do I add custom blocks? A: You can create custom blocks using code or install plugins that offer additional block types.
- Q: Is Gutenberg compatible with all WordPress themes? A: While most modern themes are compatible, older themes might require adjustments or updates.
- Q: Can I use Gutenberg on mobile devices? A: Yes, Gutenberg is responsive and works well on various devices.
- Q: Where can I find more resources to learn Gutenberg? A: The official WordPress documentation and numerous online tutorials offer extensive resources.
Resources
- Official WordPress Gutenberg Documentation
- WordPress Block Editor Handbook
- (Add other relevant and reputable resources here)
Call to Action: Beginner’s Guide To WordPress Gutenberg Editor
Start creating amazing content today with the WordPress Gutenberg editor! Explore its features, experiment with different blocks, and unleash your creativity. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between the Classic Editor and Gutenberg?
The Classic Editor uses a more traditional, text-based approach to content creation. Gutenberg, on the other hand, employs a block-based system, offering greater flexibility and visual control over page layout.
Can I switch back to the Classic Editor?
Yes, a Classic Editor plugin is available for those who prefer the older interface, although using Gutenberg is generally recommended for its enhanced features.
Where can I find more resources to learn Gutenberg?
The official WordPress Codex and numerous online tutorials and courses provide extensive resources for learning and mastering Gutenberg.
Source: shoutmeloud.com
How do I add images and videos to my posts using Gutenberg?
Simply add the “Image” or “Video” block to your post, upload your media, and customize settings like size and alignment.